RNN 不动点分析教程:FlipFlop 任务示例¶
目标: 本文档作为一份全面教程,详细介绍如何使用 FixedPointFinder 工具分析在 FlipFlop 任务上训练的 RNN。
结构:
1. 理论背景:什么是不动点?
2. 环境设置:导入脚本所需库
3. 组件定义:逐一介绍 FlipFlopData、FlipFlopRNN 和 train_flipflop_rnn 函数
4. 核心用法:演示 FixedPointFinder 的具体使用流程
1. 理论背景:什么是不动点?¶
不动点 [29, 30] 是动力系统中的核心概念。对于一个 RNN,可将其视为函数 h_t+1 = F(h_t, u_t),其中 h 为隐藏状态,u 为输入。
当 输入 u 保持恒定 (例如,在 FlipFlop 任务中无脉冲输入的“记忆”阶段,u=0)时,系统演化为 h_t+1 = F(h_t)。
一个 不动点 x* 是满足 x* = F(x*) 的状态。
稳定不动点:表现为“吸引子”。若 RNN 状态
h接近x*,最终将收敛至x*。不稳定不动点:表现为“排斥子”或“鞍点”。
核心原理:训练 RNN 完成 FlipFlop 任务。训练成功后,RNN 会为每个需要“记忆”的状态(如 [+1, +1] 或 [+1, -1])构建一个 稳定不动点 。当输入 u=0 时,RNN 状态将自动流向并稳定于这些不动点,从而实现“记忆”功能。
本教程的 目的 是使用 FixedPointFinder 工具,发现 RNN 内部“隐藏”的所有稳定不动点。
2. 导入¶
导入 flipflop_fixed_points.py 脚本中使用的所有库。
[1]:
import brainpy as bp # :cite:p:`wang2023brainpy`
import brainpy.math as bm
import jax # :cite:p:`jax2018github`
import jax.numpy as jnp
import numpy as np
import random
from canns.analyzer.visualization import PlotConfig
from canns.analyzer.slow_points import FixedPointFinder, save_checkpoint, load_checkpoint, plot_fixed_points_2d, plot_fixed_points_3d
3. 组件定义:数据、模型与训练¶
本节定义 flipflop_fixed_points.py 脚本中的三个核心组件。
3.1 组件 1:FlipFlopData 类¶
这是 flipflop_fixed_points.py 脚本中的 FlipFlopData 类。
[2]:
class FlipFlopData:
"""Generator for flip-flop memory task data."""
def __init__(self, n_bits=3, n_time=64, p=0.5, random_seed=0):
"""Initialize FlipFlopData generator.
Args:
n_bits: Number of memory channels.
n_time: Number of timesteps per trial.
p: Probability of input pulse at each timestep.
random_seed: Random seed for reproducibility.
"""
self.rng = np.random.RandomState(random_seed)
self.n_time = n_time
self.n_bits = n_bits
self.p = p
def generate_data(self, n_trials):
"""Generate flip-flop task data.
Args:
n_trials: Number of trials to generate.
Returns:
dict with 'inputs' and 'targets' arrays [n_trials x n_time x n_bits].
"""
n_time = self.n_time
n_bits = self.n_bits
p = self.p
# Generate unsigned input pulses
unsigned_inputs = self.rng.binomial(1, p, [n_trials, n_time, n_bits])
# Ensure every trial starts with a pulse
unsigned_inputs[:, 0, :] = 1
# Generate random signs {-1, +1}
random_signs = 2 * self.rng.binomial(1, 0.5, [n_trials, n_time, n_bits]) - 1
# Apply random signs
inputs = unsigned_inputs * random_signs
# Compute targets
targets = np.zeros([n_trials, n_time, n_bits])
for trial_idx in range(n_trials):
for bit_idx in range(n_bits):
input_seq = inputs[trial_idx, :, bit_idx]
t_flip = np.where(input_seq != 0)[0]
for flip_idx in range(len(t_flip)):
t_flip_i = t_flip[flip_idx]
targets[trial_idx, t_flip_i:, bit_idx] = inputs[
trial_idx, t_flip_i, bit_idx
]
return {
"inputs": inputs.astype(np.float32),
"targets": targets.astype(np.float32),
}
3.2 组件 2:FlipFlopRNN 类¶
这是 flipflop_fixed_points.py 脚本中的 FlipFlopRNN 类。
用法说明:FixedPointFinder 的 原理 是寻找 x = F(x, u)。为计算 F(x, u),它将调用 rnn_model(inputs, hidden)。
FixedPointFinder 将传入形状为 [batch, 1, n_inputs] 的 inputs 和形状为 [batch, n_hidden] 的 hidden。
因此,您的 __call__ 方法 必须 能处理 n_time == 1 的情况,并返回 (outputs, h_next)。
请参见下方代码中的 if n_time == 1: 分支,该分支专为适配 FixedPointFinder 而设计。
[3]:
class FlipFlopRNN(bp.DynamicalSystem):
"""RNN model for the flip-flop memory task."""
def __init__(self, n_inputs, n_hidden, n_outputs, rnn_type="gru", seed=0):
"""Initialize FlipFlop RNN.
Args:
n_inputs: Number of input channels.
n_hidden: Number of hidden units.
n_outputs: Number of output channels.
rnn_type: Type of RNN cell ('tanh', 'gru').
seed: Random seed for weight initialization.
"""
super().__init__()
self.n_inputs = n_inputs
self.n_hidden = n_hidden
self.n_outputs = n_outputs
self.rnn_type = rnn_type.lower()
# Initialize RNN cell parameters
key = jax.random.PRNGKey(seed)
k1, k2, k3, k4 = jax.random.split(key, 4)
if rnn_type == "tanh":
# Simple tanh RNN
self.w_ih = bm.Variable(
jax.random.normal(k1, (n_inputs, n_hidden)) * 0.1
)
self.w_hh = bm.Variable(
jax.random.normal(k2, (n_hidden, n_hidden)) * 0.5
)
self.b_h = bm.Variable(jnp.zeros(n_hidden))
elif rnn_type == "gru":
# GRU cell
self.w_ir = bm.Variable(
jax.random.normal(k1, (n_inputs, n_hidden)) * 0.1
)
self.w_hr = bm.Variable(
jax.random.normal(k2, (n_hidden, n_hidden)) * 0.5
)
self.w_iz = bm.Variable(
jax.random.normal(k3, (n_inputs, n_hidden)) * 0.1
)
self.w_hz = bm.Variable(
jax.random.normal(k4, (n_hidden, n_hidden)) * 0.5
)
k5, k6, k7, k8 = jax.random.split(k4, 4)
self.w_in = bm.Variable(
jax.random.normal(k5, (n_inputs, n_hidden)) * 0.1
)
self.w_hn = bm.Variable(
jax.random.normal(k6, (n_hidden, n_hidden)) * 0.5
)
self.b_r = bm.Variable(jnp.zeros(n_hidden))
self.b_z = bm.Variable(jnp.zeros(n_hidden))
self.b_n = bm.Variable(jnp.zeros(n_hidden))
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported rnn_type: {rnn_type}")
# Readout layer
self.w_out = bm.Variable(
jax.random.normal(k3, (n_hidden, n_outputs)) * 0.1
)
self.b_out = bm.Variable(jnp.zeros(n_outputs))
# Initial hidden state
self.h0 = bm.Variable(jnp.zeros(n_hidden))
def step(self, x_t, h):
"""Single RNN step.
Args:
x_t: [batch_size x n_inputs] input at time t.
h: [batch_size x n_hidden] hidden state.
Returns:
h_next: [batch_size x n_hidden] next hidden state.
"""
if self.rnn_type == "tanh":
# Simple tanh RNN step
h_next = jnp.tanh(
x_t @ self.w_ih.value + h @ self.w_hh.value + self.b_h.value
)
elif self.rnn_type == "gru":
# GRU step
r = jax.nn.sigmoid(
x_t @ self.w_ir.value + h @ self.w_hr.value + self.b_r.value
)
z = jax.nn.sigmoid(
x_t @ self.w_iz.value + h @ self.w_hz.value + self.b_z.value
)
n = jnp.tanh(
x_t @ self.w_in.value + (r * h) @ self.w_hn.value + self.b_n.value
)
h_next = (1 - z) * n + z * h
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown rnn_type: {self.rnn_type}")
return h_next
def __call__(self, inputs, hidden=None):
"""Forward pass through the RNN. Optimized with jax.lax.scan."""
batch_size = inputs.shape[0]
n_time = inputs.shape[1]
# Initialize hidden state
if hidden is None:
h = jnp.tile(self.h0.value, (batch_size, 1))
else:
h = hidden
# Single-step computation mode for the fixed-point finder
if n_time == 1:
x_t = inputs[:, 0, :]
h_next = self.step(x_t, h)
y = h_next @ self.w_out.value + self.b_out.value
return y[:, None, :], h_next
# Full sequence case
def scan_fn(carry, x_t):
"""Single-step scan function"""
h_prev = carry
h_next = self.step(x_t, h_prev)
y_t = h_next @ self.w_out.value + self.b_out.value
return h_next, (y_t, h_next)
# (batch, time, features) -> (time, batch, features)
inputs_transposed = inputs.transpose(1, 0, 2)
# Run the scan
_, (outputs_seq, hiddens_seq) = jax.lax.scan(scan_fn, h, inputs_transposed)
outputs = outputs_seq.transpose(1, 0, 2)
hiddens = hiddens_seq.transpose(1, 0, 2)
return outputs, hiddens
3.3 组件 3:train_flipflop_rnn 函数¶
这是 flipflop_fixed_points.py 脚本中的 train_flipflop_rnn 函数。
主要更新:
使用现代 BrainPy 优化器 API:
bp.optimizers.Adam(lr=..., train_vars=...)处理参数名称映射(
vars()返回完整名称如'FlipFlopRNN0.w_ih')不再使用
braintools或已弃用的register_trainable_weights()
[4]:
def train_flipflop_rnn(rnn, train_data, valid_data,
learning_rate=0.08,
batch_size=128,
max_epochs=1000,
min_loss=1e-4,
print_every=10):
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("Training FlipFlop RNN (Using brainpy optimizer)")
print("=" * 70)
# Prepare data
train_inputs = jnp.array(train_data['inputs'])
train_targets = jnp.array(train_data['targets'])
valid_inputs = jnp.array(valid_data['inputs'])
valid_targets = jnp.array(valid_data['targets'])
n_train = train_inputs.shape[0]
n_batches = n_train // batch_size
# Get trainable variables from the model
# Note: vars() returns keys like 'FlipFlopRNN0.w_ih', we need just 'w_ih' for computation
train_vars = {name: var for name, var in rnn.vars().items() if isinstance(var, bm.Variable)}
# Create mapping between short names and full names
name_mapping = {name.split('.')[-1]: name for name in train_vars.keys()}
# Extract just the parameter name (after the last dot) for gradient computation
params = {name.split('.')[-1]: var.value for name, var in train_vars.items()}
# Initialize optimizer with train_vars parameter (modern brainpy API)
optimizer = bp.optimizers.Adam(lr=learning_rate, train_vars=train_vars)
# Define JIT-compiled gradient step
@jax.jit
def grad_step(params, batch_inputs, batch_targets):
"""Pure function to compute loss and gradients"""
def forward_pass(p, inputs):
batch_size = inputs.shape[0]
h = jnp.tile(p['h0'], (batch_size, 1))
def scan_fn(carry, x_t):
h_prev = carry
if rnn.rnn_type == "tanh":
h_next = jnp.tanh(x_t @ p['w_ih'] + h_prev @ p['w_hh'] + p['b_h'])
elif rnn.rnn_type == "gru":
r = jax.nn.sigmoid(x_t @ p['w_ir'] + h_prev @ p['w_hr'] + p['b_r'])
z = jax.nn.sigmoid(x_t @ p['w_iz'] + h_prev @ p['w_hz'] + p['b_z'])
n = jnp.tanh(x_t @ p['w_in'] + (r * h_prev) @ p['w_hn'] + p['b_n'])
h_next = (1 - z) * n + z * h_prev
else:
h_next = h_prev
y_t = h_next @ p['w_out'] + p['b_out']
return h_next, y_t
inputs_transposed = inputs.transpose(1, 0, 2)
_, outputs_seq = jax.lax.scan(scan_fn, h, inputs_transposed)
outputs = outputs_seq.transpose(1, 0, 2)
return outputs
def loss_fn(p):
outputs = forward_pass(p, batch_inputs)
return jnp.mean((outputs - batch_targets) ** 2)
loss_val, grads = jax.value_and_grad(loss_fn)(params)
return loss_val, grads
losses = []
print("\nTraining parameters:")
print(f" Batch size: {batch_size}")
print(f" Learning rate:{learning_rate:.6f} (Fixed)")
for epoch in range(max_epochs):
perm = np.random.permutation(n_train)
epoch_loss = 0.0
for batch_idx in range(n_batches):
start_idx = batch_idx * batch_size
end_idx = start_idx + batch_size
batch_inputs = train_inputs[perm[start_idx:end_idx]]
batch_targets = train_targets[perm[start_idx:end_idx]]
loss_val, grads_short = grad_step(params, batch_inputs, batch_targets)
# Map gradients back to full names for optimizer
grads = {name_mapping[short_name]: grad for short_name, grad in grads_short.items()}
optimizer.update(grads)
# Update params with current variable values (extract parameter names)
params = {name.split('.')[-1]: var.value for name, var in train_vars.items()}
epoch_loss += float(loss_val)
epoch_loss /= n_batches
losses.append(epoch_loss)
if epoch % print_every == 0:
valid_outputs, _ = rnn(valid_inputs)
valid_loss = float(jnp.mean((valid_outputs - valid_targets) ** 2))
print(f"Epoch {epoch:4d}: train_loss = {epoch_loss:.6f}, "
f"valid_loss = {valid_loss:.6f}")
if epoch_loss < min_loss:
print(f"\nReached target loss {min_loss:.2e} at epoch {epoch}")
break
# Training complete
valid_outputs, _ = rnn(valid_inputs)
final_valid_loss = float(jnp.mean((valid_outputs - valid_targets) ** 2))
print("\n" + "=" * 70)
print("Training Complete!")
print("=" * 70)
print(f"Final training loss: {epoch_loss:.6f}")
print(f"Final validation loss: {final_valid_loss:.6f}")
print(f"Total epochs: {epoch + 1}")
return losses
4. 核心用法:训练与寻找不动点¶
我们将复现 flipflop_fixed_points.py 脚本中 main 函数与 if __name__ == "__main__": 块的逻辑。
我们将:
定义任务配置
设置参数并生成数据
训练或加载(若存在)模型
初始化并运行
FixedPointFinder打印结果并可视化
4.1 第 1 步:定义配置与参数¶
此部分源自 flipflop_fixed_points.py 中的全局 TASK_CONFIGS 字典、if __name__ == "__main__": 块,以及 main 函数的起始部分。
[5]:
# Configuration Dictionary
TASK_CONFIGS = {
"2_bit": {
"n_bits": 2,
"n_hidden": 3,
"n_trials_train": 512,
"n_inits":1024,
},
"3_bit": {
"n_bits": 3,
"n_hidden": 4,
"n_trials_train": 512,
"n_inits":1024,
},
"4_bit": {
"n_bits": 4,
"n_hidden": 6,
"n_trials_train": 512,
"n_inits":1024,
},
}
# --- Set parameters ---
# (This part is from the if __name__ == "__main__" block in the original script)
config_to_run = "3_bit" # Specify which configuration to run
seed_to_use = 42 # Use a fixed seed
config_name = config_to_run
seed = seed_to_use
# (This part is from the main function in the original script)
if config_name not in TASK_CONFIGS:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown config_name: {config_name}. Available: {list(TASK_CONFIGS.keys())}")
config = TASK_CONFIGS[config_name]
# Set random seeds
np.random.seed(seed)
random.seed(seed)
print(f"\n--- Running FlipFlop Task ({config_name}) ---")
print(f"Seed: {seed}")
n_bits = config["n_bits"]
n_hidden = config["n_hidden"]
n_trials_train = config["n_trials_train"]
n_inits = config["n_inits"]
n_time = 64
n_trials_valid = 128
n_trials_test = 128
rnn_type = "tanh"
learning_rate = 0.08
batch_size = 128
max_epochs = 500 # (Originally 1000, 500 runs faster in Notebook)
min_loss = 1e-4
--- Running FlipFlop Task (3_bit) ---
Seed: 42
4.2 第 2 步:生成数据并训练模型¶
此部分源自 flipflop_fixed_points.py 中的 main 函数。
[6]:
# Generate data
data_gen = FlipFlopData(n_bits=n_bits, n_time=n_time, p=0.5, random_seed=seed)
train_data = data_gen.generate_data(n_trials_train)
valid_data = data_gen.generate_data(n_trials_valid)
test_data = data_gen.generate_data(n_trials_test)
# Create RNN model
rnn = FlipFlopRNN(n_inputs=n_bits, n_hidden=n_hidden, n_outputs=n_bits, rnn_type=rnn_type, seed=seed)
# Check for checkpoint
checkpoint_path = f"flipflop_rnn_{config_name}_checkpoint.msgpack"
if load_checkpoint(rnn, checkpoint_path):
print(f"Loaded model from checkpoint: {checkpoint_path}")
else:
# Train the RNN
print(f"No checkpoint found ({checkpoint_path}). Training...")
losses = train_flipflop_rnn(
rnn,
train_data,
valid_data,
learning_rate=learning_rate,
batch_size=batch_size,
max_epochs=max_epochs,
min_loss=min_loss,
print_every=10
)
No checkpoint found (flipflop_rnn_3_bit_checkpoint.msgpack). Training...
======================================================================
Training FlipFlop RNN (Using brainpy optimizer)
======================================================================
Training parameters:
Batch size: 128
Learning rate:0.080000 (Fixed)
Epoch 0: train_loss = 0.934704, valid_loss = 0.716311
Epoch 10: train_loss = 0.006317, valid_loss = 0.006368
Epoch 20: train_loss = 0.000650, valid_loss = 0.000600
Epoch 30: train_loss = 0.000387, valid_loss = 0.000375
Epoch 40: train_loss = 0.000302, valid_loss = 0.000295
Epoch 50: train_loss = 0.000257, valid_loss = 0.000253
Epoch 60: train_loss = 0.000229, valid_loss = 0.000227
Epoch 70: train_loss = 0.000209, valid_loss = 0.000207
Epoch 80: train_loss = 0.000193, valid_loss = 0.000191
Epoch 90: train_loss = 0.000179, valid_loss = 0.000178
Epoch 100: train_loss = 0.000167, valid_loss = 0.000166
Epoch 110: train_loss = 0.000157, valid_loss = 0.000156
Epoch 120: train_loss = 0.000147, valid_loss = 0.000147
Epoch 130: train_loss = 0.000139, valid_loss = 0.000138
Epoch 140: train_loss = 0.000131, valid_loss = 0.000131
Epoch 150: train_loss = 0.000124, valid_loss = 0.000124
Epoch 160: train_loss = 0.000118, valid_loss = 0.000117
Epoch 170: train_loss = 0.000112, valid_loss = 0.000111
Epoch 180: train_loss = 0.000106, valid_loss = 0.000106
Epoch 190: train_loss = 0.000101, valid_loss = 0.000101
Reached target loss 1.00e-04 at epoch 193
======================================================================
Training Complete!
======================================================================
Final training loss: 0.000100
Final validation loss: 0.000100
Total epochs: 194
4.3 第 3 步:运行不动点分析¶
这是 FixedPointFinder 的 具体用法 ,源自 main 函数。
用法说明:
收集状态轨迹:
hiddens_np。FixedPointFinder将从这些“真实”状态中 采样 初始点。初始化
FixedPointFinder:rnn_model:传入rnn实例do_compute_jacobians=True:必须设为True,用于计算雅可比矩阵J = dF/dxdo_decompose_jacobians=True:必须设为True,用于计算J的特征值以判断 稳定性
运行
find_fixed_points:state_traj:传入hiddens_npinputs:我们希望寻找“记忆”状态,即 无输入 时的不动点,因此传入恒定零向量constant_input
[7]:
# Fixed Point Analysis
print("\n--- Fixed Point Analysis ---")
inputs_jax = jnp.array(test_data["inputs"])
outputs, hiddens = rnn(inputs_jax)
hiddens_np = np.array(hiddens)
# Find fixed points
finder = FixedPointFinder(
rnn,
method="joint",
max_iters=5000,
lr_init=0.02,
tol_q=1e-4,
final_q_threshold=1e-6,
tol_unique=1e-2,
do_compute_jacobians=True,
do_decompose_jacobians=True,
outlier_distance_scale=10.0,
verbose=True,
super_verbose=True,
)
constant_input = np.zeros((1, n_bits), dtype=np.float32)
unique_fps, all_fps = finder.find_fixed_points(
state_traj=hiddens_np,
inputs=constant_input,
n_inits=n_inits,
noise_scale=0.4,
)
--- Fixed Point Analysis ---
Searching for fixed points from 1024 initial states.
Finding fixed points via joint optimization.
/var/folders/x0/_jqxxbbn0rsdn6b4h6fxbrjr0000gn/T/ipykernel_3897/1298414900.py:25: UserWarning: Joint optimization with n_inits=1024 may be inefficient and use excessive memory. Consider using sequential optimization or reducing n_inits.
unique_fps, all_fps = finder.find_fixed_points(
Iter: 100, q = 2.76e-04 +/- 1.94e-03, dq = 8.52e-06 +/- 4.71e-05, lr = 2.00e-02, avg iter time = 1.18e-02 sec.
Iter: 200, q = 4.19e-05 +/- 9.01e-04, dq = 3.81e-07 +/- 6.37e-06, lr = 2.00e-02, avg iter time = 8.01e-03 sec.
Iter: 300, q = 4.77e-06 +/- 1.16e-04, dq = 1.86e-07 +/- 4.34e-06, lr = 2.00e-02, avg iter time = 6.71e-03 sec.
Optimization complete to desired tolerance.
384 iters, q = 1.06e-07 +/- 3.12e-06, dq = 5.27e-09 +/- 1.49e-07, lr = 2.00e-02, avg iter time = 6.15e-03 sec
Identified 26 unique fixed points.
Computing recurrent Jacobian at 26 unique fixed points.
Computing input Jacobian at 26 unique fixed points.
Decomposing 26 Jacobians...
Found 8 stable and 18 unstable fixed points.
Applying final q-value filter (q < 1.0e-06)...
Excluded 1 low-quality fixed points.
25 high-quality fixed points remain.
Fixed point finding complete.
4.4 结果分析与可视化¶
find_fixed_points 返回两个对象:
all_fps:包含从n_inits个初始点出发找到的所有结果unique_fps:我们最关注的结果。经tol_unique过滤后的非重复不动点集合
如何解读:
unique_fps.n:找到的独特不动点数量unique_fps.qstar:q值,越接近 0 越优unique_fps.is_stable:(关键) 是否为稳定不动点
对于 N-bit 任务,我们期望找到 2^N 个稳定不动点 (代表 2^N 种记忆状态)
下方代码单元整合了 flipflop_fixed_points.py 脚本中 main 函数末尾与 if __name__ == "__main__": 块的最后一行,用于打印全部分析结果并生成图表。
[8]:
# Print results
print("\n--- Fixed Point Analysis Results ---")
unique_fps.print_summary()
if unique_fps.n > 0:
print(f"\nDetailed Fixed Point Information (Top 10):")
print(f"{'#':<4} {'q-value':<12} {'Stability':<12} {'Max |eig|':<12}")
print("-" * 45)
for i in range(min(10, unique_fps.n)):
stability_str = "Stable" if unique_fps.is_stable[i] else "Unstable"
max_eig = np.abs(unique_fps.eigval_J_xstar[i, 0])
print(
f"{i + 1:<4} {unique_fps.qstar[i]:<12.2e} {stability_str:<12} {max_eig:<12.4f}"
)
# Visualize fixed points - 2D
config_2d = PlotConfig(
title=f"FlipFlop Fixed Points ({config_name} - 2D PCA)",
xlabel="PC 1", ylabel="PC 2", figsize=(10, 8),
show=True
)
plot_fixed_points_2d(unique_fps, hiddens_np, config=config_2d)
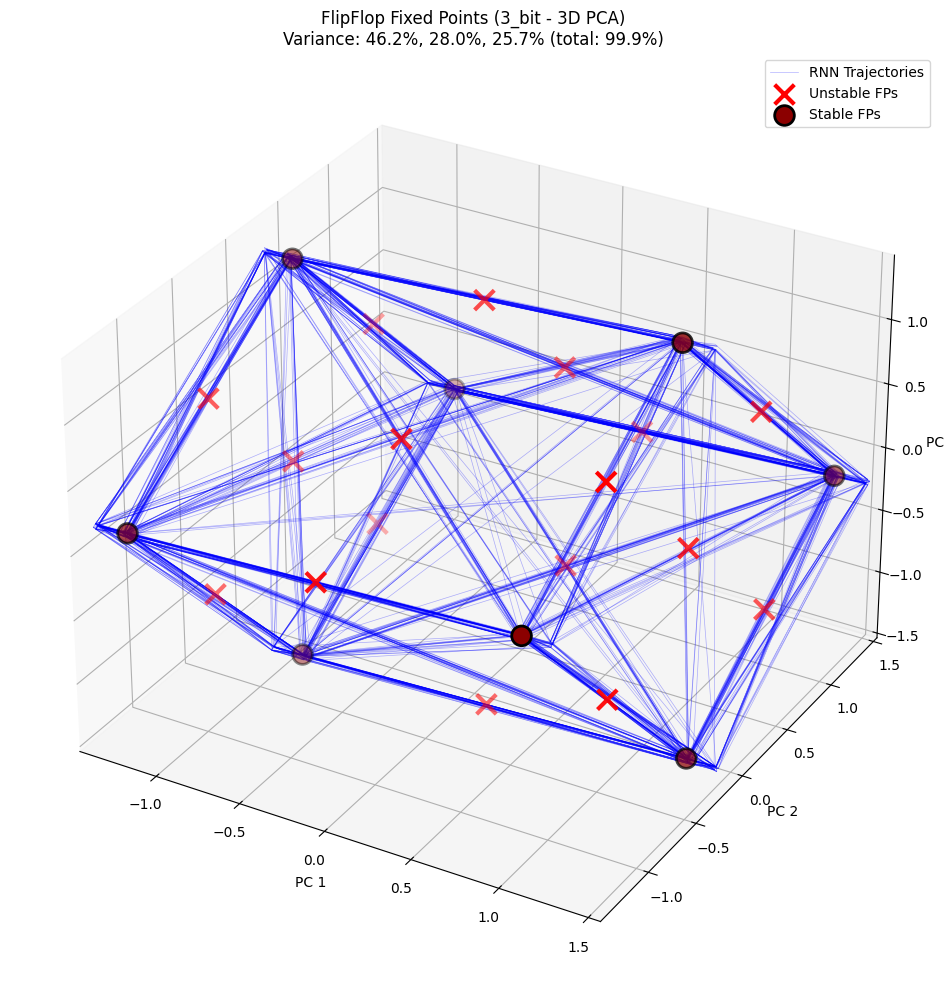
# Visualize fixed points - 3D
config_3d = PlotConfig(
title=f"FlipFlop Fixed Points ({config_name} - 3D PCA)",
figsize=(12, 10),
show=True
)
plot_fixed_points_3d(
unique_fps, hiddens_np, config=config_3d,
plot_batch_idx=list(range(30)), plot_start_time=10
)
print("\n--- Analysis complete ---")
--- Fixed Point Analysis Results ---
=== Fixed Points Summary ===
Number of fixed points: 25
State dimension: 4
Input dimension: 3
q values: min=0.00e+00, median=6.78e-19, max=9.87e-15
Iterations: min=384, median=384, max=384
Stable fixed points: 8 / 25
Detailed Fixed Point Information (Top 10):
# q-value Stability Max |eig|
---------------------------------------------
1 1.78e-15 Stable 0.2418
2 0.00e+00 Stable 0.2308
3 0.00e+00 Stable 0.2291
4 6.78e-19 Unstable 1.7985
5 1.78e-15 Unstable 2.1942
6 0.00e+00 Stable 0.2417
7 0.00e+00 Stable 0.2435
8 0.00e+00 Stable 0.2291
9 0.00e+00 Stable 0.2436
10 1.78e-15 Stable 0.2307
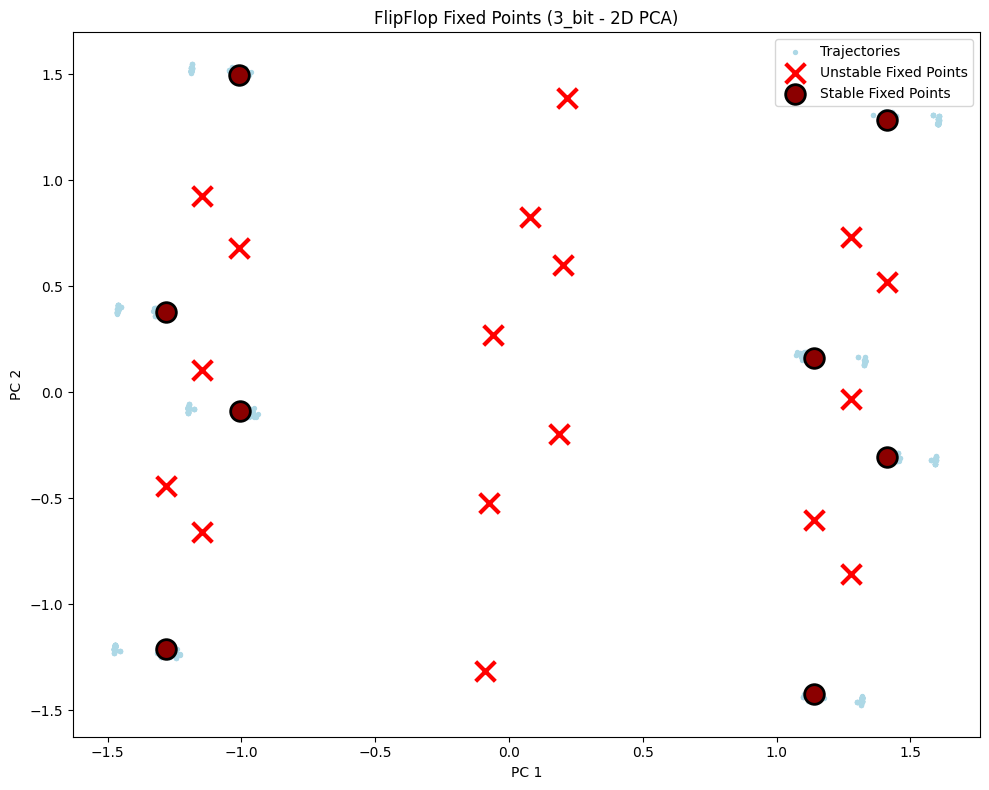
PCA explained variance: [0.46209928 0.27972662 0.25745255]
Total variance explained: 99.93%
--- Analysis complete ---
5. 多配置对比:2-bit、3-bit、4-bit¶
以下我们将运行全部三种配置,展示不同复杂度任务的不动点分析结果。
预期结果:
2-bit:4 个稳定不动点(2² = 4 种记忆状态)
3-bit:8 个稳定不动点(2³ = 8 种记忆状态)
4-bit:16 个稳定不动点(2⁴ = 16 种记忆状态)
[9]:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def run_flipflop_analysis(config_name, seed=42):
"""Run complete analysis pipeline for a single configuration"""
config = TASK_CONFIGS[config_name]
n_bits = config["n_bits"]
n_hidden = config["n_hidden"]
n_trials_train = config["n_trials_train"]
n_inits = config["n_inits"]
# Set random seeds
np.random.seed(seed)
random.seed(seed)
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"Configuration: {config_name} ({n_bits} bits, {n_hidden} hidden units)")
print(f"{'='*60}")
# Generate data
data_gen = FlipFlopData(n_bits=n_bits, n_time=64, p=0.5, random_seed=seed)
train_data = data_gen.generate_data(n_trials_train)
valid_data = data_gen.generate_data(128)
test_data = data_gen.generate_data(128)
# Create and train model
rnn = FlipFlopRNN(n_inputs=n_bits, n_hidden=n_hidden,
n_outputs=n_bits, rnn_type="tanh", seed=seed)
checkpoint_path = f"flipflop_rnn_{config_name}_checkpoint.msgpack"
if not load_checkpoint(rnn, checkpoint_path):
print(f"Training model...")
train_flipflop_rnn(rnn, train_data, valid_data,
learning_rate=0.08, batch_size=128,
max_epochs=500, min_loss=1e-4, print_every=50)
else:
print(f"Loaded model from checkpoint: {checkpoint_path}")
# Get hidden state trajectory
inputs_jax = jnp.array(test_data["inputs"])
outputs, hiddens = rnn(inputs_jax)
hiddens_np = np.array(hiddens)
# Fixed point analysis
finder = FixedPointFinder(
rnn, method="joint", max_iters=5000, lr_init=0.02,
tol_q=1e-4, final_q_threshold=1e-6, tol_unique=1e-2,
do_compute_jacobians=True, do_decompose_jacobians=True,
outlier_distance_scale=10.0, verbose=True, super_verbose=False,
)
constant_input = np.zeros((1, n_bits), dtype=np.float32)
unique_fps, _ = finder.find_fixed_points(
state_traj=hiddens_np, inputs=constant_input,
n_inits=n_inits, noise_scale=0.4,
)
return unique_fps, hiddens_np, config_name
# Store results for all configurations
all_results = {}
for cfg in ["2_bit", "3_bit", "4_bit"]:
unique_fps, hiddens_np, name = run_flipflop_analysis(cfg, seed=43)
all_results[cfg] = {"fps": unique_fps, "hiddens": hiddens_np}
# Print summary
n_stable = np.sum(unique_fps.is_stable) if unique_fps.n > 0 else 0
expected = 2 ** int(cfg[0])
print(f"\nResults: Found {unique_fps.n} fixed points, {n_stable} stable (expected: {expected})")
============================================================
Configuration: 2_bit (2 bits, 3 hidden units)
============================================================
Training model...
======================================================================
Training FlipFlop RNN (Using brainpy optimizer)
======================================================================
Training parameters:
Batch size: 128
Learning rate:0.080000 (Fixed)
Epoch 0: train_loss = 0.933466, valid_loss = 0.676156
Epoch 50: train_loss = 0.000569, valid_loss = 0.000562
Epoch 100: train_loss = 0.000369, valid_loss = 0.000366
Epoch 150: train_loss = 0.000271, valid_loss = 0.000268
Epoch 200: train_loss = 0.000210, valid_loss = 0.000208
Epoch 250: train_loss = 0.000169, valid_loss = 0.000168
Epoch 300: train_loss = 0.000139, valid_loss = 0.000138
Epoch 350: train_loss = 0.000116, valid_loss = 0.000115
Reached target loss 1.00e-04 at epoch 395
======================================================================
Training Complete!
======================================================================
Final training loss: 0.000100
Final validation loss: 0.000099
Total epochs: 396
Searching for fixed points from 1024 initial states.
Finding fixed points via joint optimization.
/var/folders/x0/_jqxxbbn0rsdn6b4h6fxbrjr0000gn/T/ipykernel_3897/1594189833.py:52: UserWarning: Joint optimization with n_inits=1024 may be inefficient and use excessive memory. Consider using sequential optimization or reducing n_inits.
unique_fps, _ = finder.find_fixed_points(
Optimization complete to desired tolerance.
170 iters, q = 9.62e-08 +/- 2.84e-06, dq = 1.36e-07 +/- 4.32e-06, lr = 1.63e-02, avg iter time = 7.56e-03 sec
Identified 9 unique fixed points.
Computing recurrent Jacobian at 9 unique fixed points.
Computing input Jacobian at 9 unique fixed points.
Decomposing 9 Jacobians...
Found 4 stable and 5 unstable fixed points.
Applying final q-value filter (q < 1.0e-06)...
9 high-quality fixed points remain.
Fixed point finding complete.
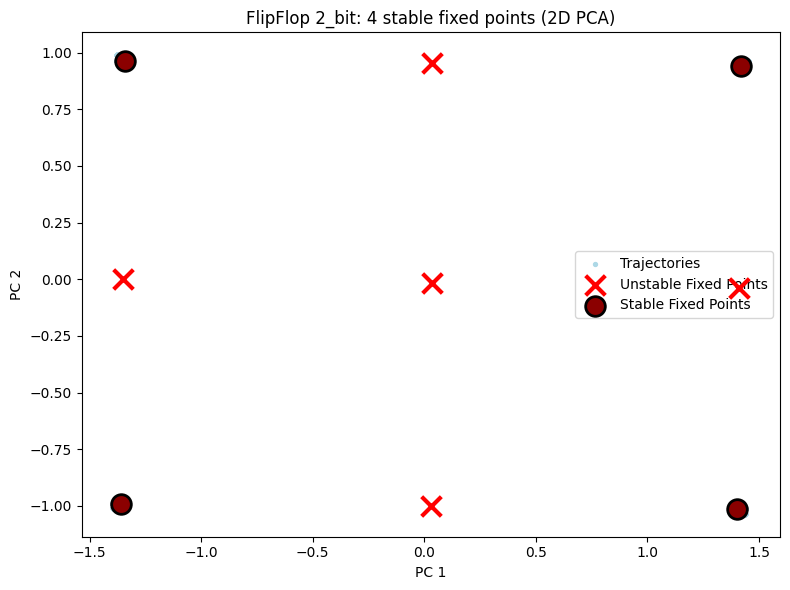
Results: Found 9 fixed points, 4 stable (expected: 4)
============================================================
Configuration: 3_bit (3 bits, 4 hidden units)
============================================================
Training model...
======================================================================
Training FlipFlop RNN (Using brainpy optimizer)
======================================================================
Training parameters:
Batch size: 128
Learning rate:0.080000 (Fixed)
Epoch 0: train_loss = 0.917904, valid_loss = 0.676378
Epoch 50: train_loss = 0.000278, valid_loss = 0.000279
Epoch 100: train_loss = 0.000161, valid_loss = 0.000163
Epoch 150: train_loss = 0.000116, valid_loss = 0.000117
Reached target loss 1.00e-04 at epoch 180
======================================================================
Training Complete!
======================================================================
Final training loss: 0.000100
Final validation loss: 0.000101
Total epochs: 181
Searching for fixed points from 1024 initial states.
Finding fixed points via joint optimization.
Optimization complete to desired tolerance.
162 iters, q = 1.36e-07 +/- 3.03e-06, dq = 1.90e-08 +/- 4.74e-07, lr = 2.00e-02, avg iter time = 4.13e-03 sec
Identified 27 unique fixed points.
Computing recurrent Jacobian at 27 unique fixed points.
Computing input Jacobian at 27 unique fixed points.
Decomposing 27 Jacobians...
Found 9 stable and 18 unstable fixed points.
Applying final q-value filter (q < 1.0e-06)...
Excluded 1 low-quality fixed points.
26 high-quality fixed points remain.
Fixed point finding complete.
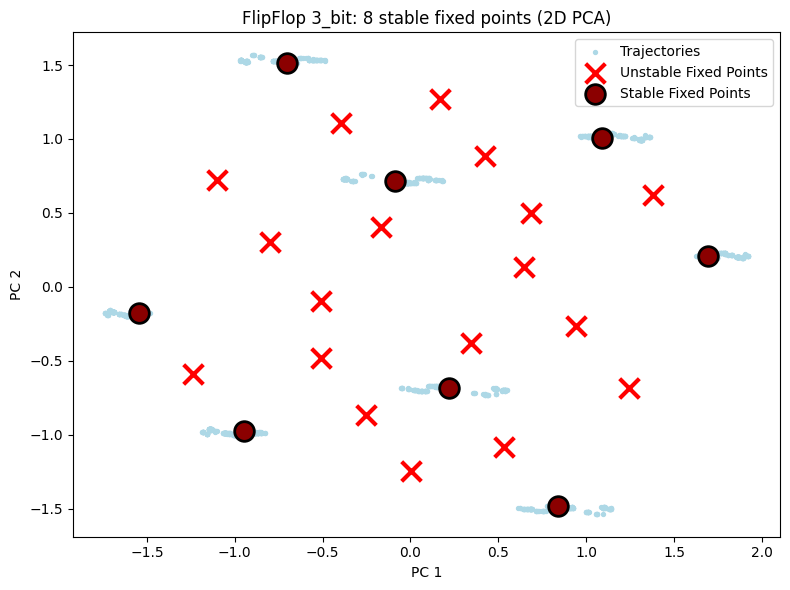
Results: Found 26 fixed points, 8 stable (expected: 8)
============================================================
Configuration: 4_bit (4 bits, 6 hidden units)
============================================================
Training model...
======================================================================
Training FlipFlop RNN (Using brainpy optimizer)
======================================================================
Training parameters:
Batch size: 128
Learning rate:0.080000 (Fixed)
Epoch 0: train_loss = 0.915913, valid_loss = 0.698172
Epoch 50: train_loss = 0.000216, valid_loss = 0.000215
Epoch 100: train_loss = 0.000131, valid_loss = 0.000130
Reached target loss 1.00e-04 at epoch 140
======================================================================
Training Complete!
======================================================================
Final training loss: 0.000100
Final validation loss: 0.000100
Total epochs: 141
Searching for fixed points from 1024 initial states.
Finding fixed points via joint optimization.
Optimization complete to desired tolerance.
333 iters, q = 4.02e-07 +/- 4.73e-06, dq = 1.24e-08 +/- 1.45e-07, lr = 2.00e-02, avg iter time = 5.46e-03 sec
Identified 74 unique fixed points.
Computing recurrent Jacobian at 74 unique fixed points.
Computing input Jacobian at 74 unique fixed points.
Decomposing 74 Jacobians...
Found 22 stable and 52 unstable fixed points.
Applying final q-value filter (q < 1.0e-06)...
Excluded 7 low-quality fixed points.
67 high-quality fixed points remain.
Fixed point finding complete.
Results: Found 67 fixed points, 16 stable (expected: 16)
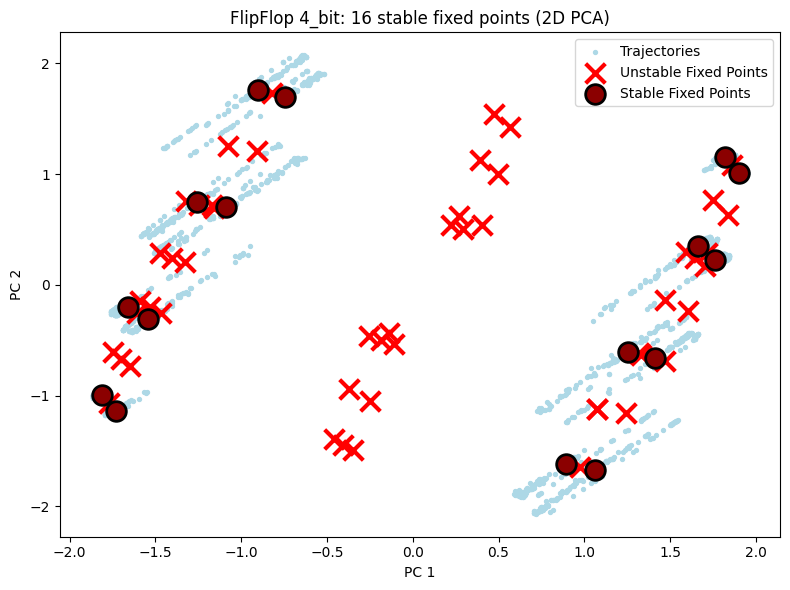
5.1 2D 可视化对比¶
展示三种配置的 2D PCA 投影,可直观观察到随任务复杂度增加,不动点数量增多。
[10]:
# 2D visualization - display each configuration separately
for cfg in ["2_bit", "3_bit", "4_bit"]:
result = all_results[cfg]
unique_fps = result["fps"]
hiddens_np = result["hiddens"]
n_bits = int(cfg[0])
n_stable = np.sum(unique_fps.is_stable) if unique_fps.n > 0 else 0
config_2d = PlotConfig(
title=f"FlipFlop {cfg}: {n_stable} stable fixed points (2D PCA)",
xlabel="PC 1", ylabel="PC 2",
figsize=(8, 6),
show=True
)
plot_fixed_points_2d(unique_fps, hiddens_np, config=config_2d)
5.2 3D 可视化对比¶
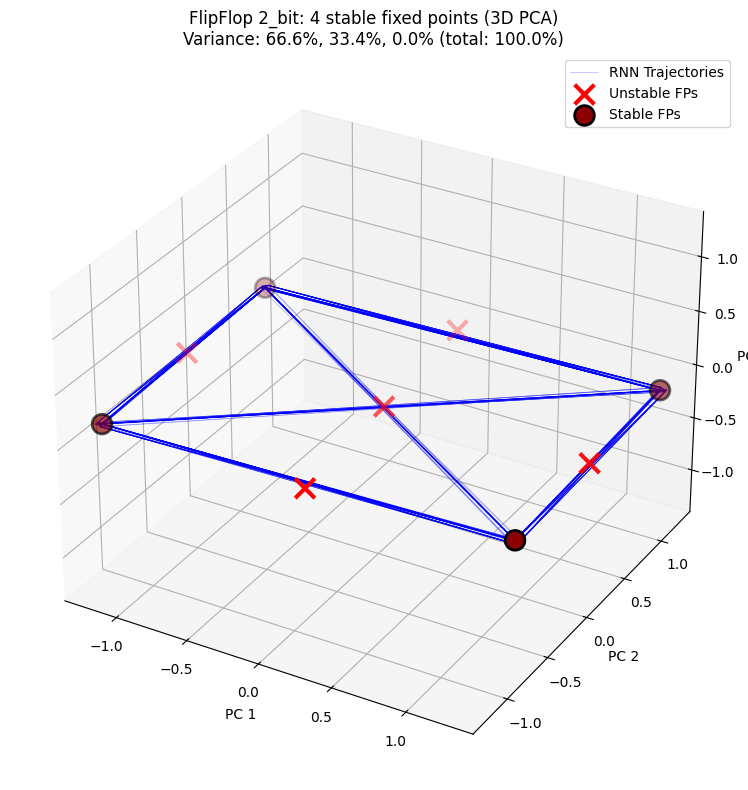
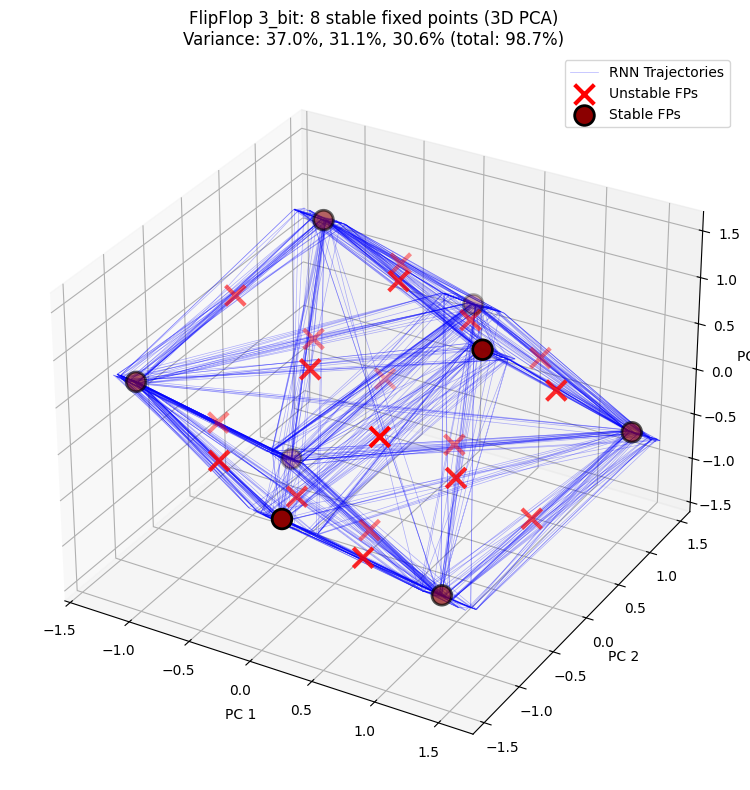
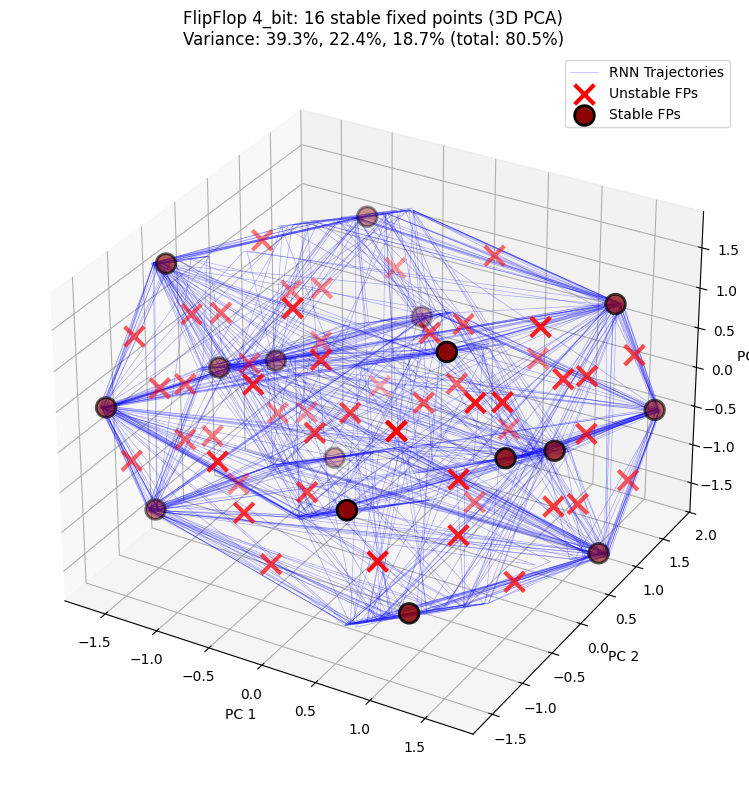
3D PCA 投影展示隐藏状态轨迹与不动点在三维空间中的分布,更清晰呈现 RNN 的动力学结构。
[11]:
# 3D visualization - display each configuration separately
for cfg in ["2_bit", "3_bit", "4_bit"]:
result = all_results[cfg]
unique_fps = result["fps"]
hiddens_np = result["hiddens"]
n_bits = int(cfg[0])
n_stable = np.sum(unique_fps.is_stable) if unique_fps.n > 0 else 0
config_3d = PlotConfig(
title=f"FlipFlop {cfg}: {n_stable} stable fixed points (3D PCA)",
figsize=(10, 8),
show=True
)
plot_fixed_points_3d(
unique_fps, hiddens_np, config=config_3d,
plot_batch_idx=list(range(20)), plot_start_time=10
)
PCA explained variance: [6.6613883e-01 3.3384740e-01 1.3795699e-05]
Total variance explained: 100.00%
PCA explained variance: [0.37013304 0.3110425 0.3062212 ]
Total variance explained: 98.74%
PCA explained variance: [0.3934802 0.22392422 0.18720938]
Total variance explained: 80.46%
6. 总结¶
本教程展示了如何使用 FixedPointFinder 分析 RNN 的动力学结构:
关键发现:
对于 N-bit 任务,RNN 学会创建 2^N 个稳定不动点
这些不动点对应不同的记忆状态组合
不动点分析是理解 RNN 内部计算机制的有力工具