教程 3: 分析与可视化方法¶
本教程介绍了 CANNs 分析器模块中的可视化与分析方法。
1. 分析器模块与 PlotConfigs 概览¶
canns.analyzer.plotting 模块为分析模拟结果提供可视化方法。所有绘图函数均使用 PlotConfigs 系统进行统一配置管理。
1.1 可用的绘图方法¶
1D 模型分析:
energy_landscape_1d_static——静态能量景观energy_landscape_1d_animation——动画能量景观raster_plot——脉冲光栅图average_firing_rate_plot——随时间变化的平均放电率tuning_curve——神经调谐曲线
2D 模型分析:
energy_landscape_2d_static——2D 静态能量景观energy_landscape_2d_animation——2D 动画能量景观
1.2 PlotConfigs 系统¶
PlotConfigs 提供针对特定方法的配置构建器。每个绘图方法均对应一个配置构建器:
from canns.analyzer.visualization import (
PlotConfigs,
energy_landscape_1d_static,
energy_landscape_1d_animation,
raster_plot,
average_firing_rate_plot,
tuning_curve,
)
# 为每个方法创建配置
config_static = PlotConfigs.energy_landscape_1d_static(
figsize=(10, 6),
title='能量景观',
show=True, # 显示图表(默认)
save_path=None # 不保存至文件(默认)
)
# 将配置传递给绘图函数
energy_landscape_1d_static(
data_sets={'r': (model.x, r_history)},
config=config_static
)
Note
此为概念性示例。实际用法将在下文第 2 节中结合真实数据演示。
主要优势:
统一接口: 所有绘图方法遵循相同模式
配置复用: 一次创建,多次使用
清晰默认值:
show=True, save_path=None适用于交互式可视化
Note
默认情况下,图表将显示(show=True)且不保存(save_path=None)。如需保存图表,请设置 save_path='filename.png'。
2. 1D 分析方法¶
我们使用 SmoothTracking1D 任务演示所有 1D 分析方法。
2.1 准备工作¶
[1]:
import brainpy.math as bm
from canns.models.basic import CANN1D
from canns.task.tracking import SmoothTracking1D
from canns.analyzer.visualization import (
PlotConfigs,
energy_landscape_1d_static,
energy_landscape_1d_animation,
raster_plot,
average_firing_rate_plot,
tuning_curve,
)
# Setup environment
bm.set_dt(0.1)
# Create model
model = CANN1D(num=256, tau=1.0, k=8.1, a=0.5, A=10, J0=4.0)
# Create smooth tracking task
# Stimulus moves from -2.0 to 2.0, then to -1.0
task = SmoothTracking1D(
cann_instance=model,
Iext=[-4.0, 4.0, -2.0, 2.0], # Keypoint positions
duration=[20.0, 30.0, 20.0], # Duration for each segment
time_step=bm.get_dt(),
)
# Get task data
task.get_data()
# Define simulation step
def run_step(t, inp):
model.update(inp)
return model.u.value, model.r.value, model.inp.value
# Run simulation
u_history, r_history, input_history = bm.for_loop(run_step, operands=(task.run_steps, task.data), progress_bar=10)
<SmoothTracking1D> Generating Task data: 700it [00:00, 1633.05it/s]
2.2 能量景观(静态)¶
energy_landscape_1d_static 绘制放电率随时间与神经元位置的变化:
[2]:
index = 200 # Time step to visualize
# Configure static energy landscape
config_static = PlotConfigs.energy_landscape_1d_static(
figsize=(10, 6),
title='Energy Landscape - Smooth Tracking',
xlabel='Time Step',
ylabel='Neuron Position',
show=True,
save_path=None
)
# Plot static energy landscape
energy_landscape_1d_static(
data_sets={'u': (model.x, u_history[index]), 'stimlulus': (model.x, input_history[index])},
config=config_static
)
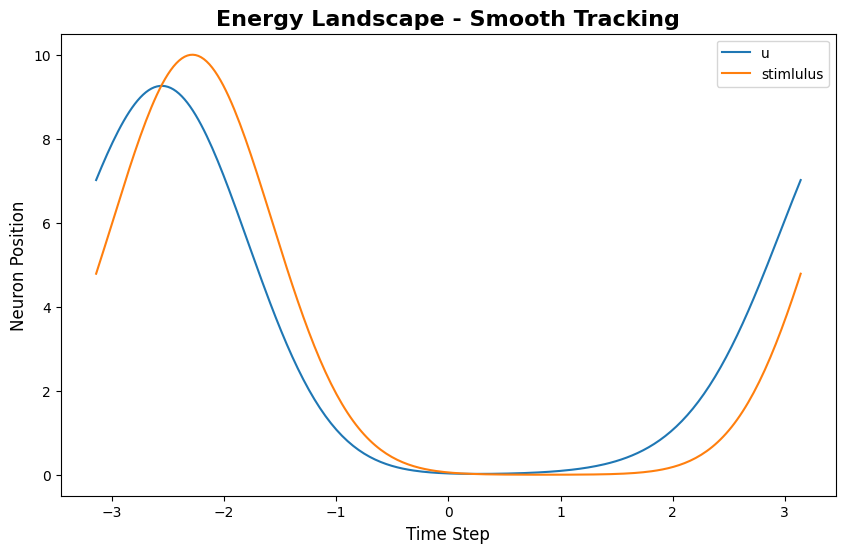
[2]:
(<Figure size 1000x600 with 1 Axes>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'Energy Landscape - Smooth Tracking'}, xlabel='Time Step', ylabel='Neuron Position'>)
该图显示了“波包”随时间的轨迹:x 轴为时间,y 轴为特征空间位置,颜色强度代表放电率。
2.3 能量景观(动画)¶
energy_landscape_1d_animation 生成动态动画,展示波包的演化过程:
[3]:
# Configure animation
config_anim = PlotConfigs.energy_landscape_1d_animation(
time_steps_per_second=100, # 100 time steps = 1 second of real time
fps=20, # 20 frames per second
title='Energy Landscape Animation',
xlabel='Neuron Position',
ylabel='Firing Rate',
repeat=True,
show=True,
save_path=None # Set to 'animation.gif' to save
)
# Generate animation
energy_landscape_1d_animation(
data_sets={'u': (model.x, u_history), 'stimlulus': (model.x, input_history)},
config=config_anim
)
动画呈现每个时间步的群体放电率分布,可视化波包如何在特征空间中移动。
动画参数:
- time_steps_per_second: 每秒真实时间对应的模拟时间步数
- fps: 动画的每秒帧数
- repeat: 是否循环播放动画
2.4 光栅图¶
raster_plot 显示神经元的脉冲发放时间:
[4]:
from canns.analyzer.metrics.utils import firing_rate_to_spike_train
# Configure raster plot
config_raster = PlotConfigs.raster_plot(
figsize=(10, 6),
title='Raster Plot',
xlabel='Time Step',
ylabel='Neuron Index',
show=True,
save_path=None
)
# use u to generate spike train, because it has higher values
spike_train = firing_rate_to_spike_train(u_history, dt_spike=0.01, dt_rate=bm.get_dt())
# Plot raster
raster_plot(
spike_train=spike_train,
config=config_raster
)
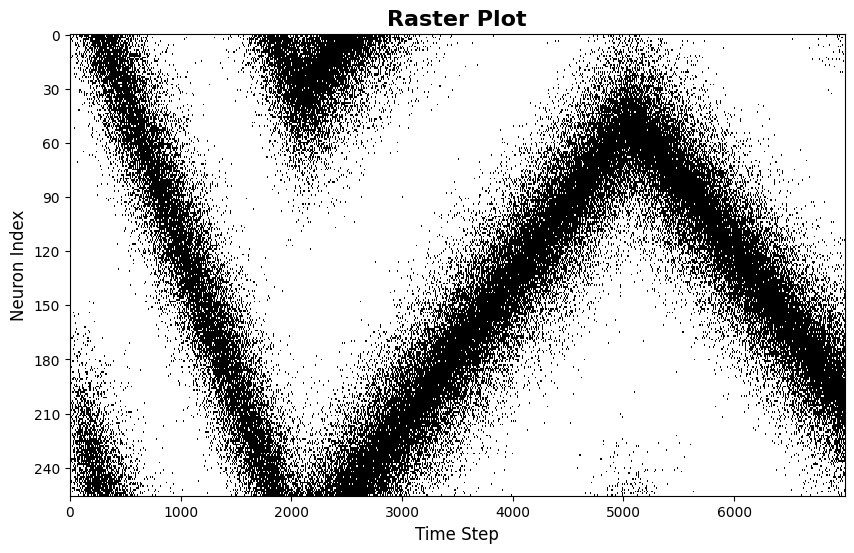
[4]:
(<Figure size 1000x600 with 1 Axes>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'Raster Plot'}, xlabel='Time Step', ylabel='Neuron Index'>)
每个点代表一个神经元在特定时刻的放电。该模式揭示了波包的空间结构及其时间演化。
2.5 平均放电率图¶
average_firing_rate_plot 显示群体平均放电率随时间的变化:
[5]:
# Configure average firing rate plot
config_avg = PlotConfigs.average_firing_rate_plot(
figsize=(10, 4),
title='Average Firing Rate',
xlabel='Time (ms)',
ylabel='Average Firing Rate',
show=True,
save_path=None
)
# Plot average firing rate
average_firing_rate_plot(
spike_train=spike_train,
dt=bm.get_dt(),
config=config_avg
)
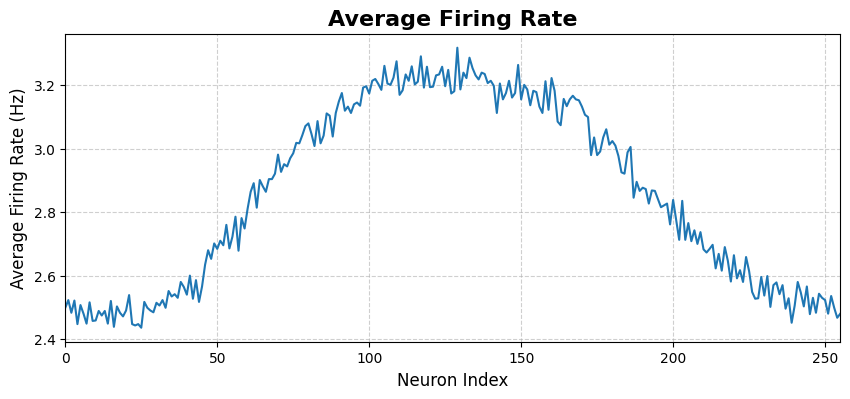
[5]:
(<Figure size 1000x400 with 1 Axes>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'Average Firing Rate'}, xlabel='Neuron Index', ylabel='Average Firing Rate (Hz)'>)
该图展示网络在一段时间内的整体活动水平。
2.6 调谐曲线¶
tuning_curve 显示单个神经元对不同刺激位置的响应:
[6]:
# Configure tuning curve
config_tuning = PlotConfigs.tuning_curve(
num_bins=50, # Number of position bins
pref_stim=model.x, # Preferred stimuli for each neuron
title='Tuning Curves of Selected Neurons',
xlabel='Stimulus Position',
ylabel='Average Firing Rate',
show=True,
save_path=None,
)
# Select neurons to plot
neuron_indices = [64, 128, 192] # Left, center, right
# Plot tuning curves
tuning_curve(
stimulus=task.Iext_sequence.squeeze(),
firing_rates=r_history,
neuron_indices=neuron_indices,
config=config_tuning
)
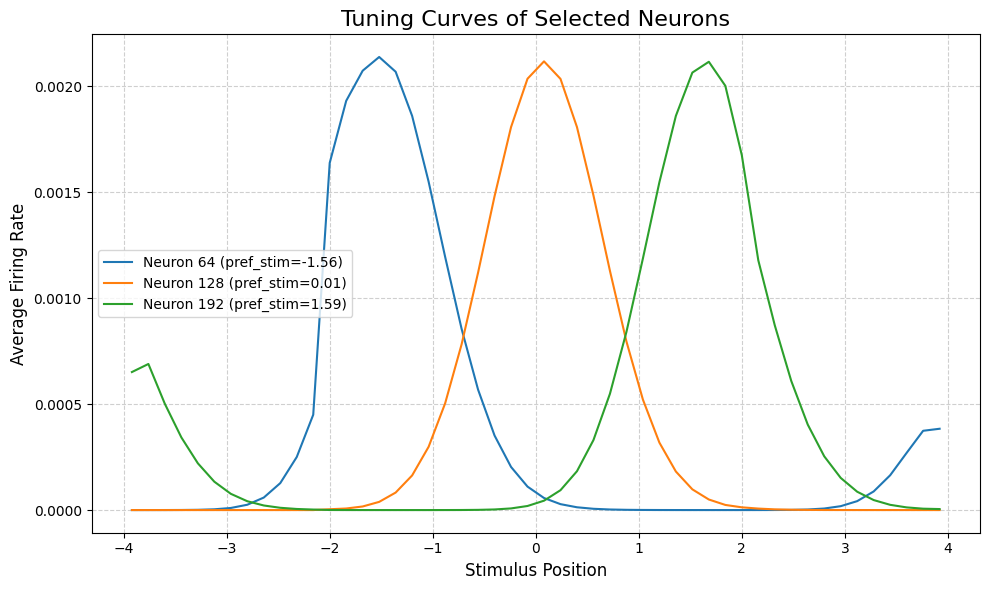
[6]:
(<Figure size 1000x600 with 1 Axes>,
<Axes: title={'center': 'Tuning Curves of Selected Neurons'}, xlabel='Stimulus Position', ylabel='Average Firing Rate'>)
调谐曲线揭示每个神经元的”偏好位置”——即引发最大响应的刺激位置。对于 CANN 模型,神经元通常具有以不同位置为中心的钟形调谐曲线。
3. 不同任务的能量景观¶
不同任务会产生特征性的能量景观模式。我们比较三种追踪任务:
3.1 PopulationCoding1D¶
群体编码展示了短暂刺激呈现后的记忆维持能力。
[7]:
from canns.task.tracking import PopulationCoding1D
model = CANN1D(num=256, tau=1.0, k=8.1, a=0.5, A=10, J0=4.0)
# Population coding task
task_pc = PopulationCoding1D(
cann_instance=model,
before_duration=10.0,
after_duration=10.0,
Iext=0.0,
duration=20.0,
time_step=bm.get_dt(),
)
# Get data and run simulation
task_pc.get_data()
u_pc, r_pc, inp_pc = bm.for_loop(run_step, operands=(task_pc.run_steps, task_pc.data), progress_bar=10)
# Visualize
config_anim = PlotConfigs.energy_landscape_1d_animation(
time_steps_per_second=100, # 100 time steps = 1 second of real time
fps=20, # 20 frames per second
title='Energy Landscape Animation - Population Coding',
xlabel='Neuron Position',
ylabel='Firing Rate',
repeat=True,
show=True,
save_path=None # Set to 'animation.gif' to save
)
# Generate animation
energy_landscape_1d_animation(
data_sets={'u': (model.x, u_pc), 'stimlulus': (model.x, inp_pc)},
config=config_anim
)
<PopulationCoding1D>Generating Task data(No For Loop)
特征模式: 波包在刺激呈现期间(中间部分)形成,并在刺激结束后仍保持在原位(右侧部分)。这体现了吸引子的稳定性与记忆维持能力。
3.2 TemplateMatching1D¶
模板匹配展示了从噪声输入中完成模式重建的能力。
[8]:
from canns.task.tracking import TemplateMatching1D
model = CANN1D(num=256, tau=1.0, k=8.1, a=0.5, A=10, J0=4.0)
# Template matching task
task_tm = TemplateMatching1D(
cann_instance=model,
Iext=1.0,
duration=50.0,
time_step=bm.get_dt(),
)
# Get data and run simulation
task_tm.get_data()
u_tm, r_tm, inp_tm = bm.for_loop(run_step, operands=(task_tm.run_steps, task_tm.data), progress_bar=10)
# Visualize
config_anim = PlotConfigs.energy_landscape_1d_animation(
time_steps_per_second=100, # 100 time steps = 1 second of real time
fps=20, # 20 frames per second
title='Energy Landscape Animation - Template Matching',
xlabel='Neuron Position',
ylabel='Firing Rate',
repeat=True,
show=True,
save_path=None # Set to 'animation.gif' to save
)
# Generate animation
energy_landscape_1d_animation(
data_sets={'u': (model.x, u_tm), 'stimlulus': (model.x, inp_tm)},
config=config_anim
)
<TemplateMatching1D>Generating Task data: 100%|██████████| 500/500 [00:00<00:00, 10877.85it/s]
特征模式: 初始的分散活动(噪声输入产生广泛而微弱的激活)收敛为一个尖锐的波包。这体现了吸引子通过收敛”清理”噪声输入的能力。
3.3 SmoothTracking1D¶
平滑追踪展示了波包跟随移动刺激的能力。
[9]:
from canns.task.tracking import SmoothTracking1D
model = CANN1D(num=256, tau=1.0, k=8.1, a=0.5, A=10, J0=4.0)
# Smooth tracking task
task_st = SmoothTracking1D(
cann_instance=model,
Iext=[-2.0, 2.0],
duration=[50.0],
time_step=bm.get_dt(),
)
# Get data and run simulation
task_st.get_data()
u_st, r_st, inp_st = bm.for_loop(run_step, operands=(task_st.run_steps, task_st.data), progress_bar=10)
# Visualize
config_anim = PlotConfigs.energy_landscape_1d_animation(
time_steps_per_second=100, # 100 time steps = 1 second of real time
fps=20, # 20 frames per second
title='Energy Landscape Animation - Smooth Tracking',
xlabel='Neuron Position',
ylabel='Firing Rate',
repeat=True,
show=True,
save_path=None # Set to 'animation.gif' to save
)
# Generate animation
energy_landscape_1d_animation(
data_sets={'u': (model.x, u_st), 'stimlulus': (model.x, inp_st)},
config=config_anim
)
<SmoothTracking1D> Generating Task data: 500it [00:00, 6982.24it/s]
特征模式: 波包平滑地从左向右移动,追踪运动刺激。这体现了吸引子在整合外部输入的同时保持稳定波包结构的能力。
3.4 对比总结¶
任务 |
输入模式 |
能量景观特征 |
演示能力 |
|---|---|---|---|
PopulationCoding |
短暂刺激 |
波包形成并原地持续 |
记忆维持 |
TemplateMatching |
噪声连续输入 |
分布式活动 → 尖锐波包 |
模式补全 |
SmoothTracking |
运动刺激 |
波包平滑跟随轨迹 |
刺激追踪 |
这三种模式揭示了连续吸引子网络的三大核心计算能力:记忆、去噪 和 追踪。
4. 2D 分析方法¶
对于 CANN2D 模型,分析器提供相应的 2D 可视化方法。PlotConfigs 模式在 2D 可视化中完全一致。
4.1 准备 CANN2D 模拟¶
[ ]:
from canns.models.basic import CANN2D
from canns.task.tracking import SmoothTracking2D
from canns.analyzer.visualization import (
PlotConfigs,
energy_landscape_2d_static,
energy_landscape_2d_animation,
)
# Create 2D model
model_2d = CANN2D(
length=32, # 32x32 neuron grid
tau=1.0,
k=8.1,
a=0.3,
A=10,
J0=4.0,
)
# Create 2D tracking task
# Move from (-1, -1) to (1, 1) to (-1, 1)
task_2d = SmoothTracking2D(
cann_instance=model_2d,
Iext=[(-1.0, -1.0), (1.0, 1.0), (-1.0, 1.0)],
duration=[30.0, 30.0],
time_step=0.1,
)
# Get data and run simulation
task_2d.get_data()
def run_step_2d(t, inp):
model_2d.update(inp)
return model_2d.u.value, model_2d.r.value
u_history_2d, r_history_2d = bm.for_loop(run_step_2d, operands=(task_2d.run_steps, task_2d.data), progress_bar=10)
<SmoothTracking2D> Generating Task data: 600it [00:00, 1153.29it/s]
4.2 能量景观 2D(静态)¶
[11]:
# Select a time point to visualize
time_idx = 300
# Configure 2D static landscape
config_2d_static = PlotConfigs.energy_landscape_2d_static(
figsize=(8, 8),
title=f'2D Energy Landscape at t={time_idx * 0.1:.1f}',
xlabel='X Position',
ylabel='Y Position',
show=True,
save_path=None
)
# Plot 2D energy landscape at specific time
energy_landscape_2d_static(
z_data=u_history_2d[time_idx],
config=config_2d_static
)
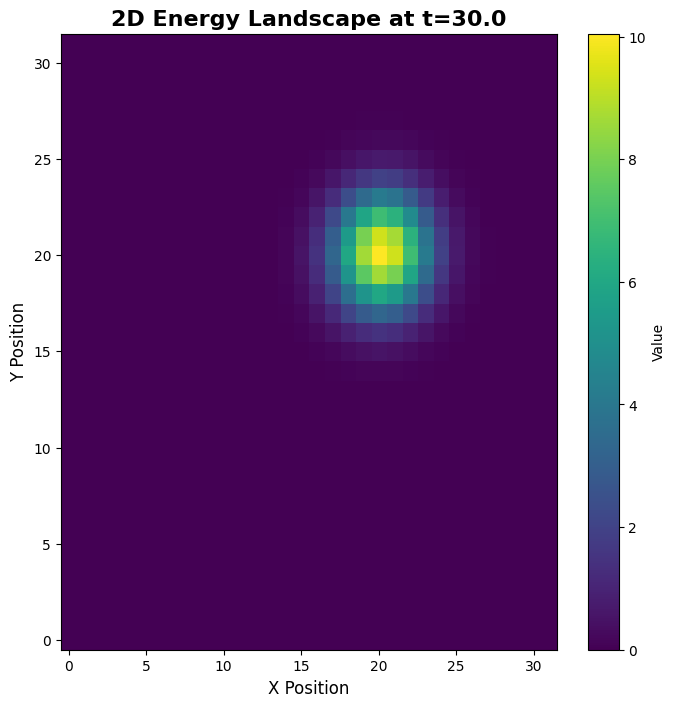
[11]:
(<Figure size 800x800 with 2 Axes>,
<Axes: title={'center': '2D Energy Landscape at t=30.0'}, xlabel='X Position', ylabel='Y Position'>)
2D 静态图显示单个时间点的放电率空间分布,揭示二维波包结构。
4.3 能量景观 2D(动画)¶
[12]:
# Configure 2D animation
config_2d_anim = PlotConfigs.energy_landscape_2d_animation(
time_steps_per_second=100,
fps=20,
figsize=(8, 8),
title='2D Energy Landscape Animation',
xlabel='X Position',
ylabel='Y Position',
repeat=True,
show=True,
save_path=None # Set to 'animation_2d.gif' to save
)
# Generate 2D energy landscape animation
energy_landscape_2d_animation(
zs_data=u_history_2d,
config=config_2d_anim
)
2D 动画展示波包在二维特征空间中沿任务定义轨迹移动的过程。
5. 下一步¶
恭喜完成教程 3!您现已掌握: - 如何使用 PlotConfigs 实现统一的可视化配置 - CANNs 中所有主要的 1D 与 2D 可视化方法 - 不同任务如何产生特征性的能量景观模式 - 三大核心计算能力:记忆、去噪与追踪
继续学习¶
下一步: 教程 4:参数效应——探索参数如何系统性影响模型行为
高级应用: 继续学习教程 5-7,了解分层模型与类脑网络
关键要点¶
PlotConfigs 模式: 始终使用
PlotConfigs.method_name()创建配置,再传递给绘图函数默认行为: 图表默认显示(
show=True, save_path=None)数据集: 所有绘图函数均接受
data_sets字典以支持灵活的数据输入任务模式: 不同任务揭示吸引子的不同属性(稳定性、收敛性、追踪能力)